Demoting Spurious Confounds in Text Classification
Despite impressive performance on many text classification tasks, deep neural networks tend to learn frequent superficial patterns that are specific to the training data and do not always generalize well. This limitation not only hurts the performance of classifiers on out-of-domain data, but also can introduce problematic biases. Our lab has worked to develop methodology that reduces the influence of confounds in text classification tasks.
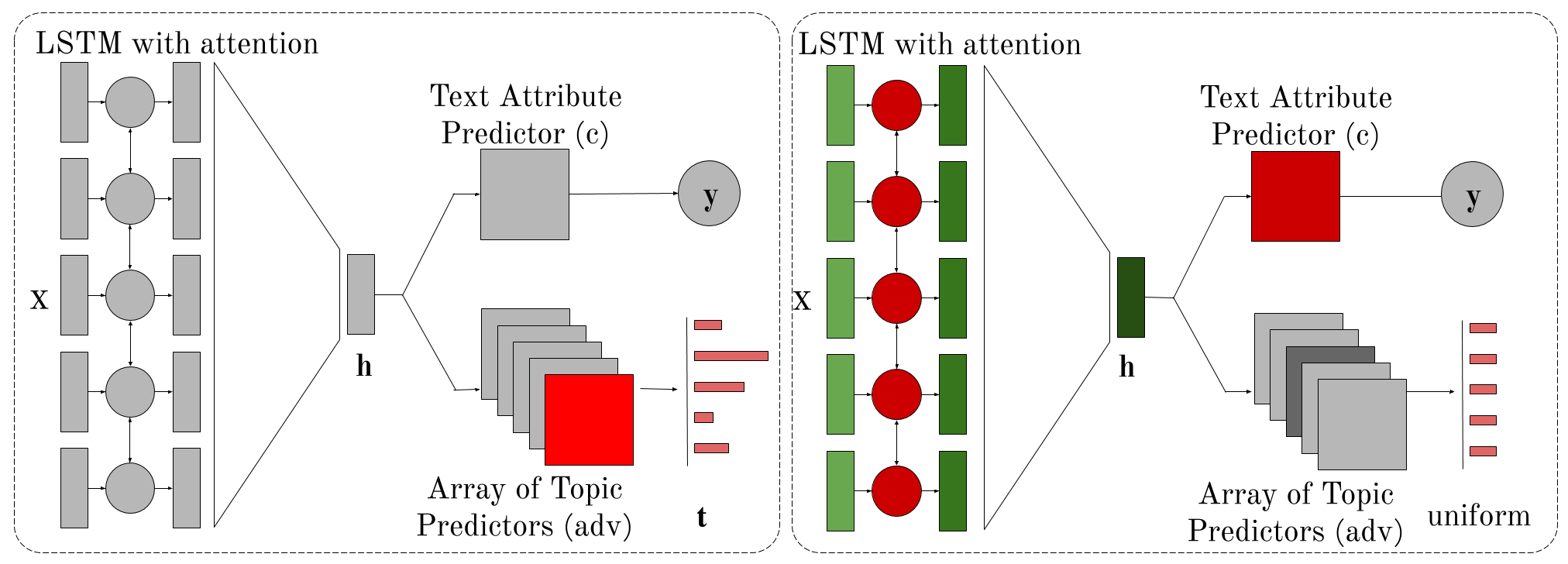
In Kumar et al. (2019), we introduce an adversarially-trained model for the task of native language identification. Standard text classifiers that perform well on the test set end up learning topical features which are confounds of the prediction task (e.g., if the input text mentions Sweden, the classifier predicts that the author’s native language is Swedish). We develop a method for representing these latent topical confounds and a prediction model that “unlearns” them by adversarially training two predictors in an alternating fashion. We show that this model generalizes better and learns features that are indicative of writing style rather than content. We additionally use this method, along with propensity matching and word substitutions, in Field and Tsvetkov (2020) in order to reduce the influence of confounding variables in the task of gender bias identification. Our work on reducing the influence of racial bias in hate speech detection also uses a model trained in an alternating adversarial fashion, which is designed to discourage the model from encoding confounds and perpetuating racial bias (Xia et al., 2020).
People
Sachin Kumar
Anjalie Field
Related Papers
- Topics to Avoid: Demoting Latent Confounds in Text Classification, (Kumar et al., 2019), EMNLP
- Demoting Racial Bias in Hate Speech Detection, (Xia et al., 2020), SocialNLP
- Unsupervised Discovery of Implicit Gender Bias, (Field and Tsvetkov, 2020), EMNLP


